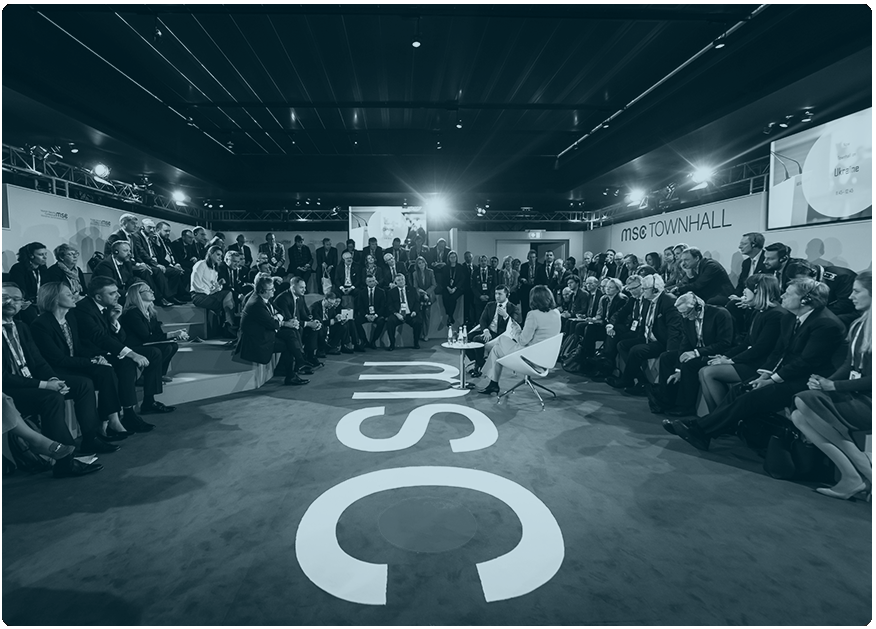


Collaborating to secure our connected world
Digitalization has transformed nearly every aspect of modern life. Today, billions of devices are connected through the Internet of Things. While this creates great opportunities, it harbours even greater risks if we are unprepared.
Founded in 2018 at the Munich Security Conference, the Charter of Trust is a global industry alliance initiated by Siemens because of increasing daily life exposure to malicious cyber-attacks.
Today, its Partners have transformed it into a unique initiative of leading global companies and organizations working together to make the digital world of tomorrow safer.
Harmonizing Global Cybersecurity
Secure the digital world by harmonizing cybersecurity approaches and addressing cybersecurity challenges from a holistic, ethical and fair perspective.
Our vision is to cultivate, advocate, and enhance global cybersecurity standards and best practices by fostering widespread awareness and ensuring a cohesive approach to security that enables seamless global interoperability.


Develop, promote, and advance the use of international harmonised cybersecurity standards and norms to secure our digital ecosystem.
Our Strategy

Trust(ed) Guidance
Lead by example through our commitment to leverage upon the use of international cybersecurity standards and norms to secure our digital ecosystem

Trust(ed) Community
Provide a platform connecting private and public organizations to share best practices, information and expertise



Trust(ed) Advice
Be a trusted partner to global governments, businesses and civil society in developing and implementing effective harmonised cybersecurity regulatory frameworks that strengthen global cybersecurity posture.
Our Approach

Build consensus, partnership, and collaboration with an international coalition of partners to define an Action Plan that tackles cybersecurity from three angles :
- ● Guidance
- ● Community
- ● Advice
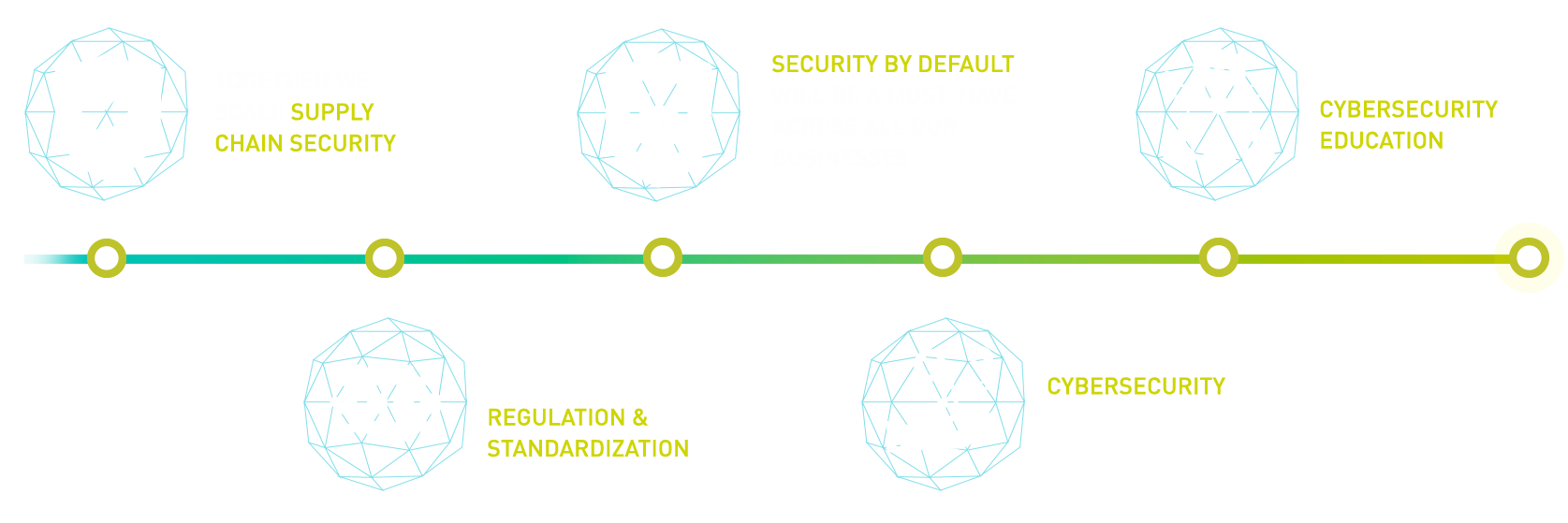
Leverage diverse expertise to address critical topics, including AI, post-quantum safety, secure and cyber-resilient digital supply chains, education (training, upskilling), and security by default.
The Charter of Trust is based on 10 key Principles that are fundamental to achieve a secure digital world.


-
Anchor the responsibility for cybersecurity at the highest governmental and business levels by designating specific ministries and CISOs. Establish clear measures and targets as well as the right mindset throughout organizations – “It is everyone’s task”.
-
Companies – and if necessary – governments must establish risk-based rules that ensure adequate protection across all IoT layers with clearly defined and mandatory requirements. Ensure confidentiality, authenticity, integrity, and availability by setting baseline standards, such as
Identity and access management: Connected devices must have secure identities and safeguarding measures that only allow authorized users and devices to use them.
Encryption: Connected devices must ensure confidentiality for data storage and transmission purposes, wherever appropriate.
Continuous protection: Companies must offer updates, upgrades, and patches throughout a reasonable lifecycle for their products, systems, and services via a secure update mechanism.
-
Adopt the highest appropriate level of security and data protection and ensure that it is preconfigured into the design of products, functionalities, processes, technologies, operations, architectures, and business models.
-
Serve as a trusted partner throughout a reasonable lifecycle, providing products, systems, and services as well as guidance based on the customer’s cybersecurity needs, impacts, and risks.
-
Combine domain know-how and deepen a joint understanding between firms and policymakers of cybersecurity requirements and rules in order to continuously innovate and adapt cybersecurity measures to new threats; drive and encourage i.a. contractual Public Private Partnerships.
-
Include dedicated cybersecurity courses in school curricula – as degree courses in universities, professional education, and trainings – in order to lead the transformation of skills and job profiles needed for the future.
-
Companies –and if necessary –governments ensure cyber-resilient products, systems, services and processes through conformity assessments including e.g., verification by independent parties.
-
Maintain and expand a network of experts who share new insights and information on incidents to foster collective cybersecurity; engage with regulators and other stakeholders on threat intelligence sharing policy and exchange best practices.
-
Promote multilateral collaborations in regulation and standardization to set a level playing field matching the global reach of WTO; inclusion of rules for cybersecurity into Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
-
Drive joint initiatives including all relevant stakeholders in order to implement the above principles in the various parts of the digital world without undue delay.
Our collaboration has shown results.



The Charter of Trust consists of global cross-industry companies and associated partners committed to securing the digital world by adhering to our 10 principles.
These partners include regulators, research institutes, universities, and think tanks from around the world, all working together to address the challenges of cybersecurity and build a safer digital future.
Together, we shape Cybersecurity.
Our Partners are joining forces to protect our democratic and economic values against cyber and hybrid threats. In this Charter, the signing partners outline the key principles we consider essential for establishing a new charter of trust between society, politics, business partners, and customers.
A strong network supporting our mission
The Charter of Trust Associated Partners are regulators, research institutes, universities, and think tanks supporting and promoting the work of the Charter of Trust. Together, we build a trusted network committed to creating a strong digital security environment across the global economy. Our Associated Partners provide valuable insights to the work of our Partners, to assess cyber trends and developments, and to work together on specific Charter of Trust projects.